Model agencies industry report
There are not so many reports and researches of modeling industry. I found only one, to be honest. According to IBISWorld Industry Report “Model Agencies in the US”:
Market overview:
- The largest segment for the Model Agencies industry is the consumer goods market. Businesses, such as cosmetics and apparel companies, frequently hire models for promotional and marketing purposes. Models are featured in advertisements in magazines, newspapers, television, billboards and other types of media. In total, this category is estimated to comprise 64.0% of total industry revenue.
- The publishing market is expected to account for 17.0% of total industry revenue in 2014. Model agencies generate revenue, either through commissions or direct fees, when their models are hired to do photo-shoots for catalogs and editorial magazines.
- Model agencies provide essential services for fashion designers, as models are often booked for runway work, which involves modeling at fashion shows. These shows primarily take place in Paris, Milan, London or New York City. This market is estimated to comprise 6.5% of total industry revenue.
- 12.5% — model agencies either receive commissions or charge fees to businesses that hire under-contract models for promotional events, such as trade shows, conferences, concerts, sporting events and festivals. During the past five years, demand for promotional models rapidly increased.
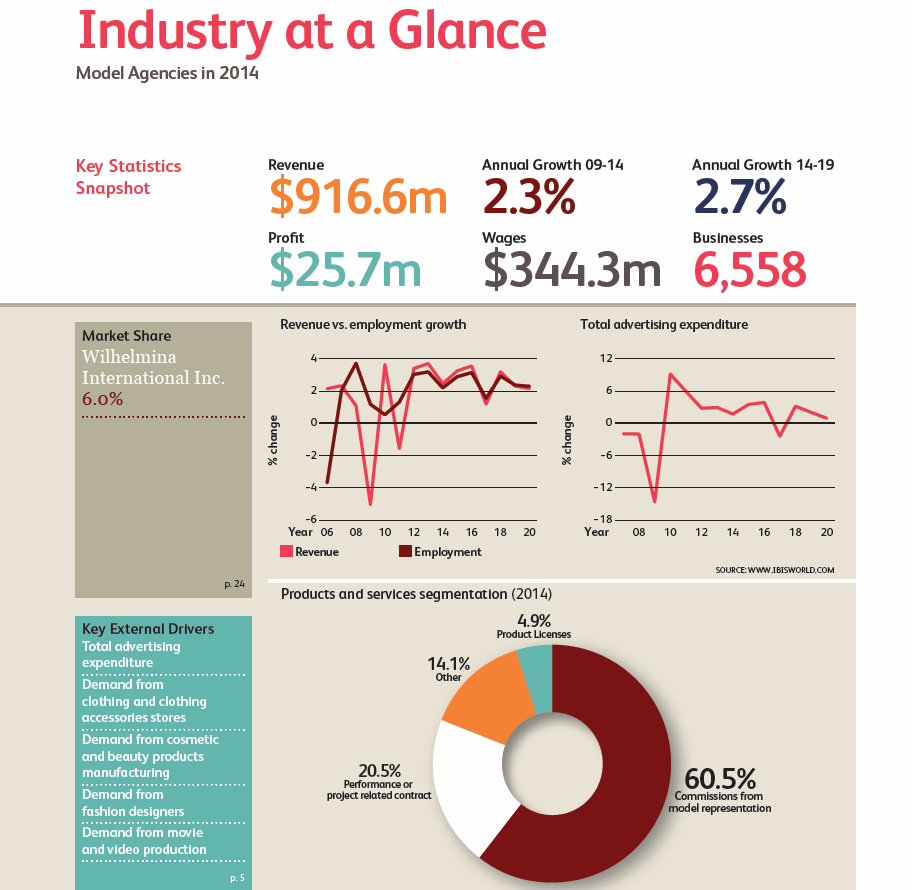
- The Model Agencies is highly fragmented. Accordingly, the industry has a low level of market share concentration, with the top four model agencies expected to account for less than 17.0% of total industry revenue. Although large, established agencies commonly attract talent through reputation, name recognition and connections to vital downstream markets, most model agencies compete on commissions, fees and other factors. In addition, the majority of industry operators are small companies or independent agents; the average industry establishment has less than two employees. Furthermore, the growing popularity of social media and online technology has made it easier for models to self-promote and independent agents to scout for new talents. As a result, industry concentration is expected to remain low during the next five years.
- The industry has benefited from the rising popularity of digital and mobile media platforms during the past five years. Models have long been the mainstay of television advertisements, representing cosmetics, clothing and other consumer products. However, emerging technologies and high competition provided an incentive for model agencies to develop new revenue streams, such as online promotional campaigns. For example, Ford Models, the predominant model agency in New York until the modeling boom in the 1980s, has been an early adopter of promotional videos on YouTube. The agency produced videos featuring their models to promote various fashion and consumers products online. Social media platforms, such as Facebook, Instagram and Twitter, have also provided model agencies new avenues to grow their business. Facebook offers similar advertising opportunities for promotional videos, while Twitter allows models to endorse and promote products. However, while agencies have been able to develop new business opportunities for digital technology, social media has also posed a threat to industry operators. Through social media, models have an easier time promoting themselves and advertisers have an easier time finding talent, thereby cutting out the middle man. At the same time, social media further lowered barriers to entry for industry operators. The growing use of social media, therefore, has augmented this industry’s fragmentation and put pressure on already-thin profit margins for model agencies.
- However, high internal competition and low barriers to entry pressured industry margins in the five years to 2014. Rising industry participation has led to pricing pressures for modeling commissions and fees, while rising employment has facilitated an increase in wage-related costs. Prior to the emergence of this technology, the bulk of industry establishments were small, independent agents. The emergence of social media and the opportunity for online self-promotion has, therefore, cut demand for these smaller agencies, as advertisers can directly seek out models for promotional companies.
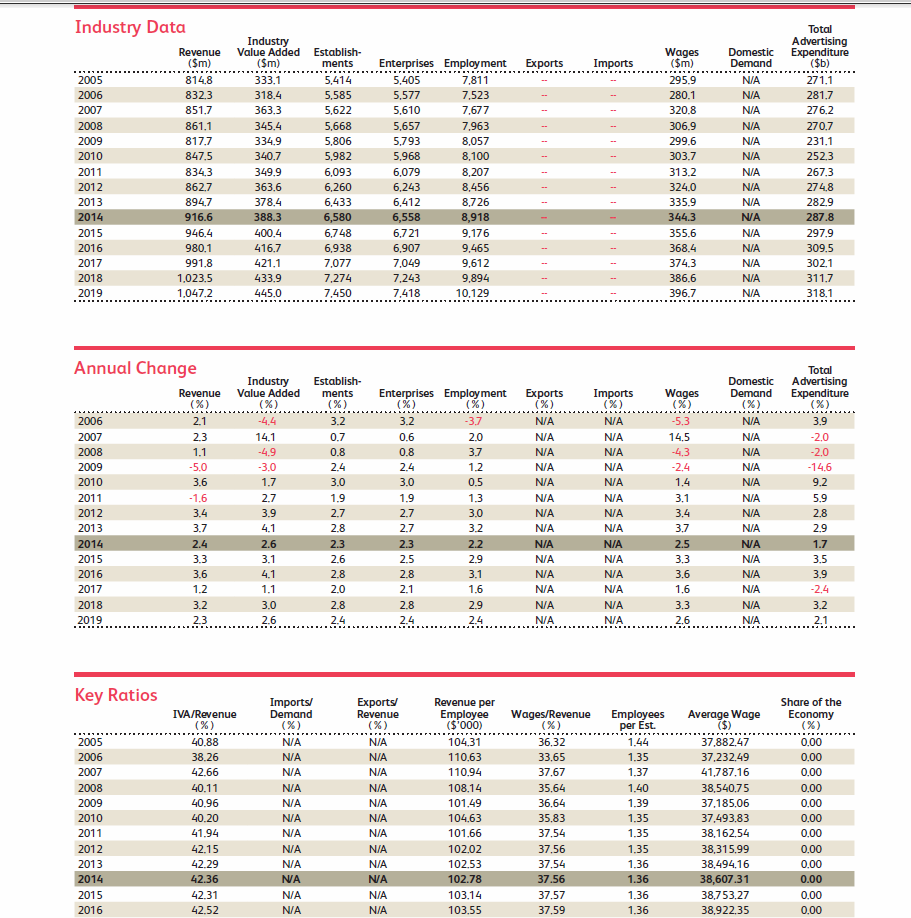
- The Model Agencies industry is anticipated to experience strengthenedgrowth over the five years to 2019. As economic growth continues, advertising spending will increase and stimulate demand for model services. In particular, major downstream markets, such as fashion designers, cosmetics manufacturers, clothing retailers and entertainment, are all anticipated to steadily grow, compared with the previous five years where many downstream markets slowly recovered in the years following the recession. In addition, unemployment is projected to slowly decline and disposable income is expected to increase. As a result, consumer spending will steadily increase, which will provide an incentive for businesses to increase advertising spending. Total advertising expenditure is projected to increase at an average annual rate of 2.0% in the five years to 2019.
- Industry enterprises will continue to face high levels of internal competition, especially as social media further expands. More models will look to represent and promote themselves online, which will make it more difficult for agencies to sign top talent. Additionally, more companies are projected to enter this industry as revenue falls. In the five years to 2019, the number of enterprises is forecast to increase at an average annual rate of 2.5% to 7,418 agencies, the bulk of which are small independent agents. As such, industry operators will continue to experience downward pressure on profit margins, similar to the previous five years. Industry wage costs are also expected to increase, because agencies have to compete to attract the best talent scouts and agents.
- Actively using technologies, such as social networking sites, can help showcase an agency’s models, increase marketing and promote brand name recognition, which is important to industry success.
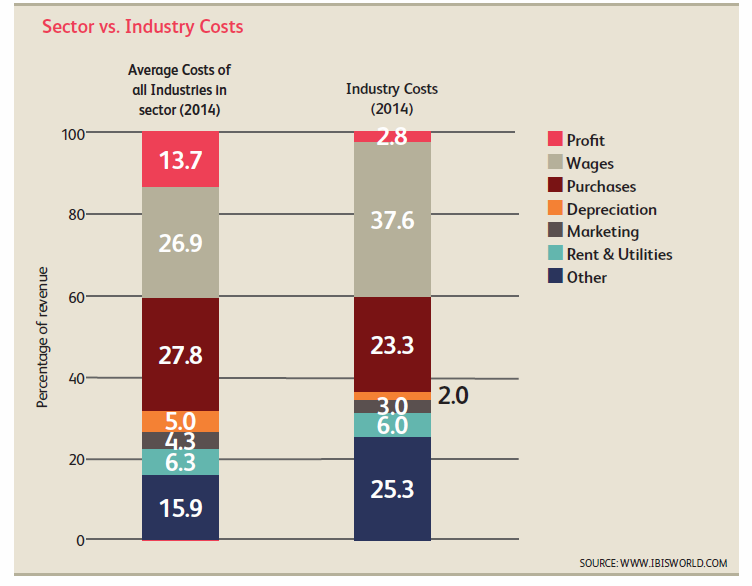
- Agents, talent scouts and other employees are needed to supply the services offered by model agencies. As a result, wages are the large cost for industry operators, accounting for about 37.6% of revenue in 2014. Agents and managers typically have expertise in sales, law, marketing, event management, licensing, TV production, promotions, account management and customer service. Premier clients may have multiple agents dedicated to managing their business interests. Demand for employees who are skilled at digital media campaigns also increased over the past five years. Wage costs moderately increased over the past five years, as agencies had to compete to hire top talent in order to attract top level models and clients.
- Purchases are estimated to account for 23.3% of industry revenue in 2014. Purchase costs primarily include corporate entertainment, travel and accommodations, talent scouting events, fashion shows and other promotional efforts.
- Model agencies may have considerable insurance expenses. Model agencies may also outsource talent scouting and other related services. As such, other expenses are estimated to total 25.3% of revenue.
- Model agencies largely compete on quality of service and court repeat business based on client satisfaction. Homogeneity of services, high competition and low industry concentration, leaves little room for price competition, especially between the industry’s largest players. Therefore,hiring qualified and experienced agents with established industry connections is vital for agency success.
- Capital intensity and regulatory barriers in this industry are low. The major barrier to entry in this industry is establishing name recognition. The industry’s largest agencies have existing relationships with fashion designers, publishers, studios and cosmetic and consumer goods companies. Having a good reputation, an established client list and proven modeling talent is essential for success in this industry. Small agencies can compete successfully by specializing in a particular field of modeling and developing relationships with targeted or niche customers. Small agencies will also find it easier to operate in geographic regions that are not dominated by the industry’s largest companies. The advancement of new media and technology, such as social networking, has made it easier for smaller industry participants to build their brand name, promote their modeling talent and generate a following of potential clientele.
- Model agencies with international expertise and reach will be more desirable, as foreign models have been increasingly hired to work in the United States over the past five years. Consequently, industry globalization is expected to continue to increase over the next five years, as demand for this industry’s services is forecast to increase both domestically and abroad.
- The Model Agencies industry has gone through a lot of technological change in the past few years. Advances in digital and social media have changed the ways agencies conduct business by broadening distribution channels, while simultaneously increasing competition. Social and digital media platforms are providing operators with a number of opportunities. It enables them to advertise their services and attract talent through a new, more public platform (i.e. Facebook). Clients can now seek industry services for projects beyond traditional media, such as magazines and television. Therefore, the market for modeling agencies has broadened. At the same time these advances have begun to cannibalize the industry’s traditional markets, as print media’s share or industry revenue continues to lose out (the same predictions reported by PwCand McKinsey). However, in spite of all of the opportunities that have arisen, social and digital media have also created threats for the industry. It is now much easier for models to advertise themselves, as well as for advertisers to find models. As a response to this challenge and to take advantage of what new media has to offer, industry operators like Wilhemina have invested in expanding their in-house art and social media departments. Companies can still increase the value of their services by capitalizing on high-end art and editing technology, thus discouraging both models and clients from looking elsewhere.
- New IT systems have also lowered the costs of doing business and increased efficiency. Some of them offers agencies and models an all-inclusive front and backend technology solution. They provide clients with website creation and management services, combined with digital photo delivery billing and accounting systems, all integrated under one platform. This kind of technology reduces administrative expenses and makes it easier for companies to operate.
· Biggest players:
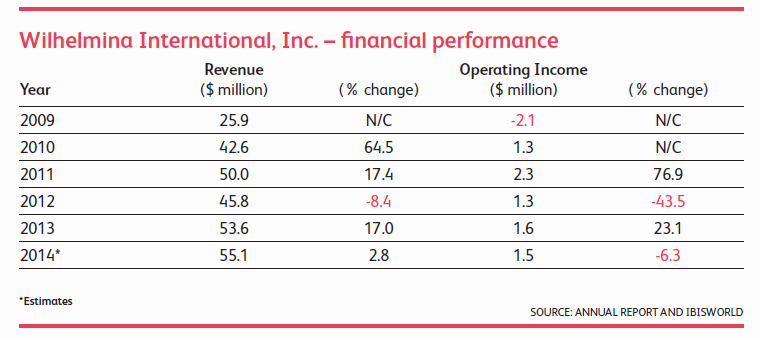
o Wilhelmina International, Inc. (formerly Wilhelmina Models — 6% of the market in the US) manages more than 1,700 models and oversees their relationships with about 2,000 clients. The company employs 92 people. In addition to model management, Wilhelmina also makes some revenue from talent management services for high-profile celebrities; this revenue is not relevant to this industry and historically accounts for just under 12.0% of the company’s total revenue. In its model management business, Wilhelmina makes revenue both from models (a commission based on a percentage of the model’s gross earnings) and from clients (a service charge based on a percentage of the model’s booking fees). Most Wilhelmina models are signed to strict three-year contracts.
- IMG Models Estimated market share: 4.3%. IMG Models is a division of the global talent business IMG Worldwide Holdings (formerly known as International Management Group), headquartered in New York City. IMG Worldwide employs more than 3,500 people globally, although their model management division is only one of fourteen different business segments. In December 2013, private equity firm Silver Lake Partners and music, literary and comedy talent agency William Morris Endeavor Entertainment LLC purchased an ownership stake in IMG Worldwide Holdings for roughly $2.3 billion. The company has represented such high-profile clients as Tyra Banks, Cindy Crawford and Kate Moss. Moreover, a significant portion of IMG Models’ revenue is generated in the more than 30 countries, other than the US, in which IMG operates. In 2014, IMG Models’ US revenue to total $39.5 million.
- Ford Models Estimated market share: 3.8%. Today, the company employs about 140 people. Altpoint Capital Partners (formerly Stone Tower Equity Partners) has owned 93.0% of the company since 2007; in that time Ford has expanded its business offerings to include management services for other fashion professionals, such as makeup artists, designers, stylists and photographers. Ford Models’ US industry-relevant revenue to total $35.5 million.
- DNA Model Management Estimated market share: 2.7%. DNA currently represents such high-profile models as Linda Evangelista, Natalia Vodianiva and Doutzen Kroes. The company has taken an unusual approach to structuring their model management business, aiming to maintain a certain size that allows it to offer the personalized service of a smaller boutique agency while retaining the business and financial skills of a large company. The enterprise’s US revenue to total an estimated $24.5 million in 2014.
- Elite World S.A. Estimated market share: 1.6%. The company went public on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange in 2006 (their 2006 report) — and delisted with valuation 13,2M euro (history of stock price), 15–20x times lower, than on peak. Elite World’s businesses are divided into three main business segments: Elite Model Management, which scouts and develops models for long-term contracts; Elite Licensing; and Elite Model Look, which is an international fashion modeling contest and event. In 2012, Elite World established The Society Model Management, the company’s first fully owned subsidiary in the US. In the short time since The Society has debuted, the company has successfully drawn major bookers and agents from established New York agencies. Following this expansion, in December 2013, Elite World established Women Management Inc. bolstering the company’s presence in the New York model management scene and the Model Agencies industry. As of year-end 2013 (most recent company information), Elite World S.A. reported $14.6 million in revenue for its US operations.
One more (but very old report):
Some additions:
I can suggest, that if US market estimated as $0,9B of annual revenue — than, worldwide market (also UK, Japan, Italy, France, and regional hubs — China, Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea, etc) is about $4–5B. But it is only model agencies revenue — total turnover of model contracts will be about $10B. Also catwalks, advertorials and commercials include many other talents — hair and makeup artists, photographers, etc. — we can estimate a market opportunity of $20–25B.
Comments
Post a Comment